CW021A
Ring
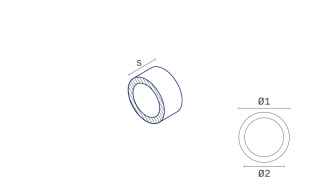
- Form Ring
- Material Kupfer
- Werkstoff CW021A
- Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 Cu-HCP
Unternehmen der BIKAR Metals


Leiter für Elektronik und Elektrotechnik
Superleiter-Matrizes
Kokillen für Strangguss
Kaltfließpressteile
Druckkessel
Strom-, Sammel- und Zuführungsschienen
Teile, bei denen gute Hartlöt- und Schweißbarkeit verlangt sind
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
| Bi (von) | 0,0005 |
| Bi (bis) | 0,0005 |
| Cu Fußnoten Referenz | Einschließlich Silber bis max. 0,015 %. |
| Andere | 0,03 |
| P (von) | 0,002 |
| P (bis) | 0,007 |
| Pb (von) | 0,005 |
| Pb (bis) | 0,005 |
| Rest | Cu |
| geeignet nach DIN EN 602 | Nein |
| Luftfahrt | Nein |
| Hartlöten | 1 |
| Weichlöten | 1 |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 100°C | 16,9 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 200°C | 17,3 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Wärmeausdehnungskoeffizient von 20 bis 300°C | 17,6 K⁻¹10⁻⁶ |
| Dichte | 8,94 g/cm³ |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 100°C | 119 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 20°C | 115 GPa |
| Elastizitätsmodul bei 200°C | 91 GPa |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 100°C | 43,6 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 57 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifische elektrische Leitfähigkeit bei 200°C | 33,7 m/Ω*mm² |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 100°C | 0,0229 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 20°C | 0,0169 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifischer elektrischer Widerstand bei 200°C | 0,0297 Ω*mm²/m |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 100°C | 0,393 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 20°C | 0,385 J/(kg·K) |
| Spezifische Wärme bei 200°C | 0,403 J/(kg·K) |
| Wärmeleitfähigkeit bei 20°C | 385 W/m*K |
| Gas | 4 |
| Laser | 3 |
| MIG | 2 |
| Widerstandspunktschweißen | 5 |
| WIG | 2 |
| Werkstoff chemisch EN 573-3 | Cu-HCP |
| Werkstoff Nr. | CW021A |
1 sehr gut
2 gut
3 mäßig
4 schlecht
5 ungeeignet
0 keine Angabe
